A treadmill stress test is a common and incredibly valuable diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess heart health, particularly in individuals suspected of having coronary artery disease or those looking to evaluate their exercise capacity. It involves monitoring a patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, and electrocardiogram (ECG) while they walk on a treadmill, gradually increasing the intensity of the exercise. The insights gained from this procedure can guide treatment plans and provide crucial information about a person’s cardiovascular fitness.
However, the real power of this test isn’t just in conducting it, but in effectively documenting its findings. A well-structured report translates complex physiological data into actionable information for physicians, cardiologists, and other medical staff. It serves as a permanent record, allowing for comparison over time and ensuring continuity of care. Without a clear and comprehensive report, the value of the test can be significantly diminished, potentially leading to misunderstandings or missed details.
That’s why having a robust and standardized approach to documentation is so essential. Whether you are a seasoned cardiologist or a medical student learning the ropes, utilizing an effective treadmill stress test report template can streamline the reporting process, ensure all critical data points are captured, and ultimately enhance the quality of patient care. It helps ensure consistency and clarity, making it easier for anyone reviewing the report to quickly grasp the patient’s condition and the test’s implications.
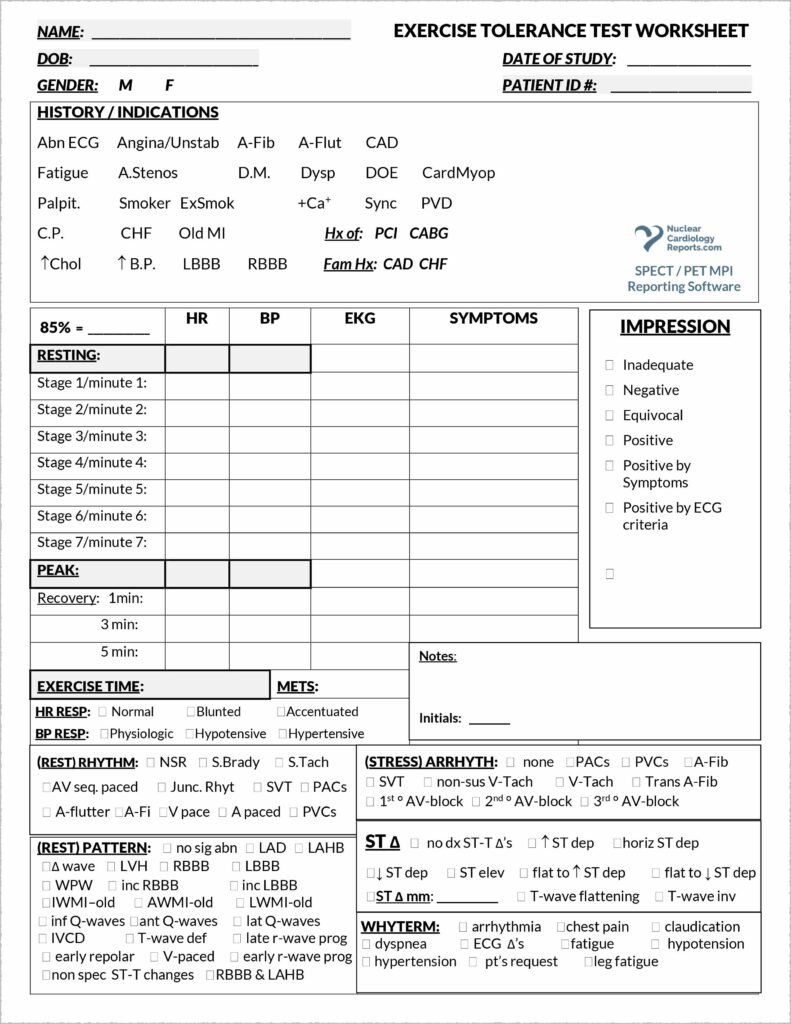
Understanding the Core Components of a Comprehensive Treadmill Stress Test Report
Crafting an effective report for a treadmill stress test goes beyond simply noting down numbers. It involves a systematic presentation of data, observations, and professional interpretation that collectively paints a complete picture of the patient’s cardiac response to exercise. A comprehensive report ensures that all relevant information is available for current and future medical decisions, preventing oversights and fostering clear communication among the medical team. This meticulous documentation is the backbone of informed clinical practice.
Patient Demographics and Clinical History
The starting point for any medical report is identifying the patient and understanding their background. This section typically includes vital details such as the patient’s full name, age, gender, height, weight, and the referring physician’s name. Crucially, it also incorporates a summary of the patient’s relevant medical history, including presenting symptoms (e.g., chest pain, shortness of breath), known cardiac conditions, current medications, risk factors for heart disease (e.g., smoking, diabetes, hypertension), and any prior cardiac interventions or tests. This context is invaluable for interpreting the stress test results.
Test Protocol and Procedures
This part of the report details how the test was performed. It specifies the particular stress test protocol used, such as the widely recognized Bruce protocol, Modified Bruce, or Naughton protocol, each having different increments of speed and incline. Additionally, it documents the preparation steps, including the patient’s fasting status, any medication adjustments made prior to the test, and the successful placement of ECG leads. Recording the exact procedure ensures reproducibility and helps in understanding the conditions under which the heart was stressed.
Key Observations During the Test
During the actual exercise phase, a multitude of physiological parameters are constantly monitored and recorded. This section of the report summarizes these critical observations, providing a snapshot of the patient’s response to exertion. It details the peak heart rate achieved, the blood pressure response throughout the test (baseline, peak, and recovery), and any significant ECG changes, such as ST-segment depression or elevation, or the occurrence of arrhythmias. The patient’s subjective symptoms, like chest pain, dizziness, or fatigue, are also documented, along with their duration and severity. This is often where a lot of quantitative data resides.
- Resting and Peak Heart Rate (BPM)
- Blood Pressure Response (Systolic and Diastolic) at various stages
- ECG Findings (ST segment changes, arrhythmias, PR interval, QRS duration)
- Symptom Description (e.g., chest pain, dyspnea, lightheadedness)
- Exercise Duration and Estimated Metabolic Equivalents (METs)
- Reason for Test Termination (e.g., target heart rate achieved, symptoms, significant ECG changes)
Interpretation and Impression
This is arguably the most critical section of the report, where the physician synthesizes all the collected data into a coherent clinical assessment. The interpretation includes whether the test was positive, negative, or inconclusive for ischemia, the patient’s exercise capacity, the presence and nature of any arrhythmias, and the heart rate and blood pressure recovery patterns. The overall impression provides a concise summary of the findings, including any limitations of the test. A well-crafted interpretation in a treadmill stress test report template provides clear clinical guidance and is essential for subsequent patient management.
Benefits of Using a Standardized Treadmill Stress Test Report Template
The adoption of a standardized template for reporting treadmill stress tests offers numerous advantages that extend across various facets of healthcare delivery. It moves beyond just creating a document; it elevates the entire process of cardiac diagnostics, ensuring consistency, improving efficiency, and enhancing the quality of care provided to patients. By structuring the information, a template serves as a consistent guide for clinicians, ensuring no critical step or data point is overlooked during the reporting phase.
One of the primary benefits is the assurance of comprehensive data collection. A well-designed template acts as a checklist, prompting medical staff to input all necessary patient details, test parameters, and physiological observations. This systematic approach minimizes the risk of missing vital information that could be crucial for an accurate diagnosis or a future comparative analysis. Furthermore, standardization improves consistency across reports generated by different clinicians or at different facilities, which is incredibly valuable for inter-provider communication and longitudinal patient care.
Moreover, utilizing a template significantly boosts efficiency in the clinical workflow. Instead of drafting each report from scratch, clinicians can quickly populate predefined fields, saving valuable time that can be redirected towards direct patient interaction or other essential tasks. This efficiency translates into quicker turnaround times for reports, allowing for more timely diagnostic and therapeutic interventions. Ultimately, the use of a standardized treadmill stress test report template contributes to better patient outcomes by ensuring clarity, completeness, and prompt access to crucial cardiac assessment information.
- Ensures Comprehensive Data Capture
- Promotes Consistency in Reporting Across Clinicians and Facilities
- Enhances Efficiency by Streamlining the Documentation Process
- Improves Clarity and Readability for All Healthcare Professionals
- Facilitates Regulatory Compliance and Accurate Record-Keeping
- Aids in Effective Communication and Collaboration Among the Medical Team
In the complex landscape of cardiac diagnostics, accurate and thorough documentation is not merely a formality; it is a fundamental pillar of patient care. The detailed recording of a patient’s response to a treadmill stress test provides invaluable insights into their cardiovascular health, guiding crucial decisions about their ongoing treatment and lifestyle recommendations. This meticulous approach ensures that every nuance of the test is captured and communicated effectively.
Embracing a structured methodology for generating these reports, perhaps through the consistent application of a well-designed template, significantly elevates the quality and utility of the information. It ensures that healthcare providers have access to complete, consistent, and easily interpretable data, ultimately leading to more informed diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved health outcomes for individuals undergoing cardiac evaluation.



