Navigating the complexities of ISO 27001 certification can feel like a marathon, not a sprint. A crucial part of this journey involves conducting regular internal audits to ensure your Information Security Management System (ISMS) is not only compliant but also continuously improving. These audits are your organization’s health check, revealing areas of strength and identifying where you might need to bolster your defenses. However, merely conducting an audit isn’t enough; the real value lies in how you document and communicate your findings.
Without a clear, consistent, and comprehensive way to report audit outcomes, even the most thorough internal audit can lose its impact. Imagine trying to track progress, assign responsibilities, or demonstrate due diligence to external auditors if your findings are scattered or poorly articulated. This is where a well-structured reporting mechanism becomes your best friend, transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive real security enhancements.
That’s why understanding and utilizing an effective iso 27001 internal audit report template is so vital. It’s not just about ticking boxes; it’s about providing a clear roadmap for improvement, ensuring accountability, and ultimately, strengthening your organization’s information security posture. Let’s dive into what makes an outstanding report and how you can leverage a template to achieve audit reporting excellence.
What Exactly Goes into a Great ISO 27001 Internal Audit Report?
So, you’ve completed an internal audit, meticulously reviewing controls, interviewing personnel, and scrutinizing documentation. Now comes the part where you distill all that effort into a coherent report. A truly great audit report isn’t just a collection of notes; it’s a strategic document that clearly communicates the audit’s purpose, the evidence gathered, the findings, and most importantly, actionable recommendations. It acts as a bridge between the technical details of the audit and the strategic decisions that need to be made by management.
Think of your report as telling a story – the story of your ISMS’s current state. It needs a beginning (scope and objectives), a middle (methodology and findings), and an end (conclusions and recommendations). Each section plays a vital role in ensuring the report is understood by various stakeholders, from technical teams who need specific details to executive management who require a high-level overview of risks and progress.
Essential Sections You Can’t Miss
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of the audit’s purpose, key findings, and overall conclusion, designed for busy executives.
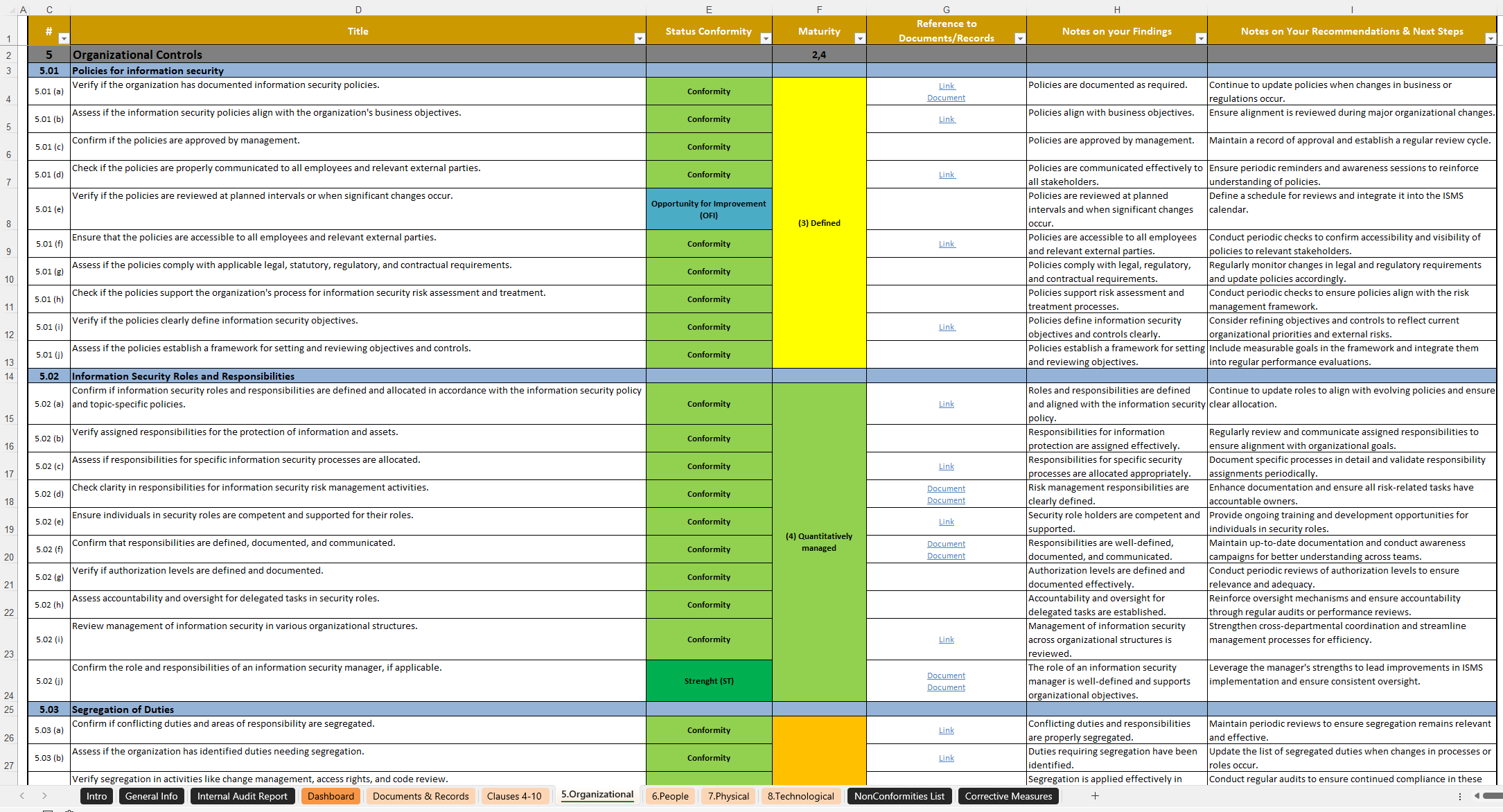
- Audit Scope and Objectives: Clearly define what was audited, which clauses of ISO 27001 were covered, and the specific goals of the audit.
- Audit Methodology: Describe how the audit was conducted, including techniques used (interviews, document review, observation) and the period covered.
- Findings (Nonconformities, Observations, Strengths): Detail specific findings, categorizing them as nonconformities (major/minor), observations (potential issues), or areas of strength. Each finding should be supported by clear evidence.
- Recommendations: For each nonconformity or observation, provide practical and actionable recommendations for corrective or improvement actions.
- Action Plan Status (if follow-up): If this is a follow-up audit, report on the status of previously agreed-upon actions.
- Auditor Details: Name(s) of the auditor(s), date of the report, and distribution list.
The “Findings” section is often the most critical part of your report. Here, precision is paramount. Avoid vague statements. Instead, clearly describe the nonconformity or observation, reference the specific ISO 27001 clause or control requirement it relates to, and provide concrete evidence to support your claim. For instance, instead of saying “Access controls are weak,” you would state, “Nonconformity: Employees were observed sharing generic login credentials for the financial system, contravening control A.9.2.2 of ISO 27001 Annex A, as evidenced by user interviews conducted on [date] and system logs from [date].”
Following a clear finding, your “Recommendations” section must offer solutions that are both practical and impactful. These aren’t just suggestions; they are the stepping stones towards addressing the identified issues. Each recommendation should be clear, measurable where possible, and assigned to a responsible party, setting the stage for effective corrective action planning and follow-up.
And remember, while the details are important, the Executive Summary is what often gets read first, and sometimes, only. It should effectively summarize the entire report, giving the reader a snapshot of your ISMS’s health and the most pressing issues that require attention. It’s your chance to grab management’s attention and convey the urgency or success of the audit.
Crafting Your Own Template for Success
While various generic templates for ISO 27001 internal audit reports exist, the real magic happens when you tailor one to your organization’s specific context. Every company has unique information assets, risk profiles, and operational complexities. A one-size-fits-all approach might miss critical nuances, making your audit report less effective in driving meaningful change.
Developing your own bespoke template doesn’t mean starting from scratch. You can take an existing structure and customize it to reflect your ISMS’s scope, your internal auditing program’s maturity, and the typical findings you encounter. Consider the language and terminology commonly used within your organization to ensure maximum clarity and buy-in from all stakeholders. The goal is to create a living document that evolves with your ISMS, making each audit more efficient and insightful than the last.
- Review your ISMS context: What are your organization’s specific security objectives and risks? Ensure your template covers these areas.
- Define your audit program: How often do you audit? What areas are typically covered? Align your template with your recurring audit cycles.
- Incorporate feedback from previous audits: What information was missing? What was unclear? Use past experiences to refine your template.
- Keep it simple and user-friendly: A template that is overly complex or difficult to complete will deter auditors and reduce the quality of reporting.
Ultimately, a well-crafted and consistently used iso 27001 internal audit report template becomes a powerful tool in your information security arsenal. It standardizes your reporting process, ensures no critical details are overlooked, and facilitates clear communication across all levels of your organization. By investing time in developing and refining your template, you’re not just creating a document; you’re building a foundation for continuous improvement and a stronger security posture.
The internal audit report isn’t merely a formality; it’s a vital communication tool that translates the technical findings of your audit into actionable intelligence. It informs management decisions, guides corrective actions, and serves as documented evidence of your commitment to maintaining a robust Information Security Management System. By meticulously detailing your findings and recommendations, you empower your organization to proactively address vulnerabilities and strengthen its security defenses.
Embracing a structured approach to your internal audit reporting ensures consistency, clarity, and accountability. This continuous cycle of auditing, reporting, and acting on findings is the cornerstone of an effective ISMS, moving your organization ever closer to information security excellence and sustained compliance with ISO 27001.